1. For measuring chemical shift in NMR spectroscopy the chemical compound commonly used as reference is
A) tetramethyl silane
B) hydroquinone
D) ethanol

2. Which of the following radiation is employed to study vibrational spectrum of a molecule?
A) Infrared radiation
B) microwave radiation
D) Ultraviolet radiation
3. Which of the following techniques can be used to study conformational changes in Myoglobin?
i) Mass spectrometry ii) Florescence spectroscopy
iii) Light Microscopy iv) Circular dichroism spectroscopy
A) i, ii
B) ii, iii
C) ii, iv
D) i, iv
4. Infrared (IR) spectroscopy is used for determining certain aspects of the structure of organic compounds. Which of the following statement(s) is/are True?
A) IR radiation induces electronic transitions
B) IR peak intensities are related to molecular mass
C) Most organic functional groups absorb in a characteristic region of the IR spectrum
D) Each element absorbs at a characteristic wavelength
5. Which of the following spectroscopic technique is / are correctly matched with the radiations
used for their study?
(i) Vibrational Spectroscopy – IR waves
(ii) Electron Spectroscopy – Gamma rays
(iii) NMR Spectroscopy – Radio waves
A) Only (i) and (ii)
B) Only (i) and (iii)
C) Only (ii) and (iii)
D) All of the above
6. The splitting signals in NMR is due to :
A) Shielding effect
B) spin spin decoupling
D) spin spin coupling
7. The NMR active molecule is
A) 6C12
B) 6C13
C) 2He1
D) 8O16
8. Which one of the following techniques relies on the spin angular momentum of a photon?
i) CD spectroscopy
ii)
iv) Raman spectroscopy
A) i, ii
B) ii, iii
C) iii, iv
D) i, iv
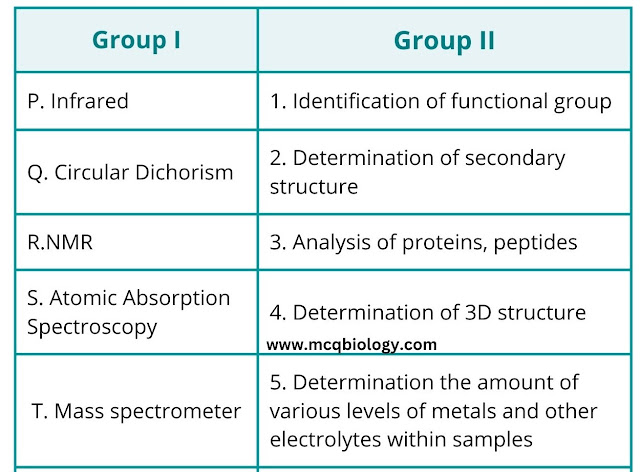
9. Which one of the following techniques can be used to determine the structure of a 15kDa globular protein at atomic resolution?
A) P-1, Q-2, R-3, S-4, T-5
B) P-1, Q-3, R-4, S-2, T-5
C)P-1, Q-2, R-4, S-5, T-3
D)P-5, Q-3, R-2, S-4, T-1
11.In Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy, which of the following is the generally used radiation source?
A) Hollow cathode lamp
B) Tungsten lamp
C) Mercury lamp
D) Hydrogen discharge lamp
12.Which of the following is the principle of Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy?
A) colour is measured
B) radiation is measured
C) Medium absorbs radiation and transmitted radiation is measured
D)Radiation is absorbed by non excited atoms in vapour state and excited to higher states
Answers:
1.A) tetramethyl silane
2. A) Infrared radiation
3. C) ii, iv
4. C) Most organic functional groups absorb in a characteristic region of the IR spectrum
5. B) Only (i) and (iii)
6. D) spin spin coupling
7. B) 6C13
8. D) i, iv
9. B) NMR spectroscopy
10. C)P-1, Q-2, R-4, S-5, T-3
11. A)Hollow cathode lamp
12. D)Radiation is absorbed by non excited atoms in vapour state and excited to higher states