1. Which statements best explains the evolutionary advantage of meiosis?
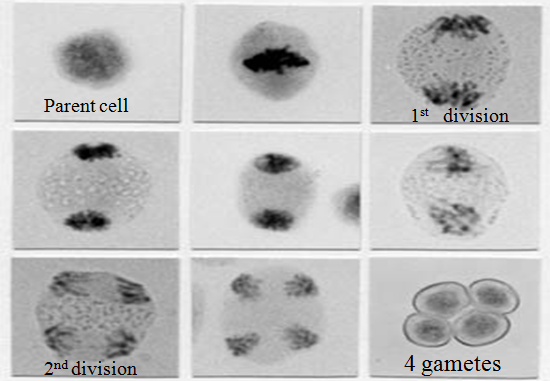
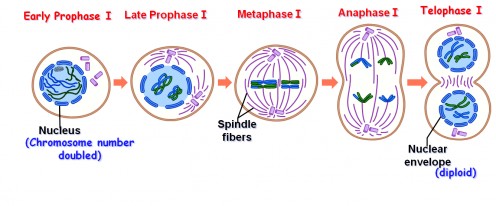
4. Meiosis II performs

a) Meiosis is necessary for sexual reproduction2. Meiotic division occurs in
b) Meiosis alternates with mitosis from generation to generation
c) The same genetic system is passed on from generation to generation
d) Genetic recombination are possible from generation to generation

a) vegetative cells3. Meiosis I is reductional division. Meiosis II is equational division due to
b) meristematic cells
c) conductive cells
d) reproductive cells

a) Crossing over
b) Separation of chromatids
c) Pairing of homologous chromosomes
d) Disjunction of homologous chromosomes
4. Meiosis II performs

a) Separation of sex chromosomes5. Segregation of Mendelian factor (Aa) occurs during
b) Synthesis of DNA and centromere
c) Separation of homologous chromosomes
d) Separation of chromatids
a) Diplotene6. Synapsis occurs between
b) Zygotene/ Pachytene
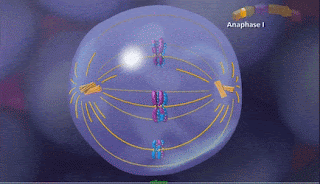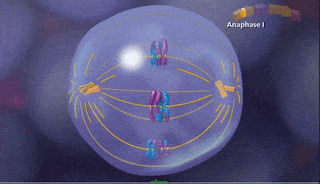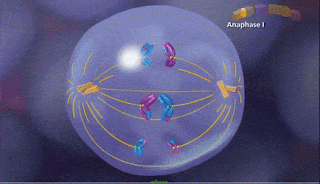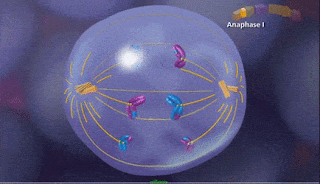
c) Anaphase I
d) Anaphase II
a) mRNA and ribosomes7. In Meiosis, the daughter cells differ from parent cell as well as amongst themselves due to
b) Spindle fibres and cetromere
c) a male and a female gamete
d) Two homologous chromosomes
a) Segregation, independent assortment and crossing over8. During which stage of prophase I of the crossing over takes place ?
b) Segregation and crossing over
c) Independent assortment and crossing over
d) Segregation and independent assortment

a) Leptotene9. Continuous variations are attributed to
b) Pachytene
c) Zygotene
d) Diplotene
a) Polyploidy
b) Mutation
c) Crossing over
d) Chromosomal aberrations
10. When parental and maternal chromosomes change their materials with each other in cell division this event called
a) synapsisLearn more
b) Crossing over
c) Dyad forming
d) Bivalent forming
- MCQ on Cell Cycle
- Practice Test on Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis (Set 1)
- Practice Test on Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis (Set 2)
Answers
1. d) Genetic recombination are possible from generation to generation
2. d) reproductive cells
3. b) Separation of chromatids
4. d) Separation of chromatids
5. c) Anaphase I
6. d) Two homologous chromosomes
7. a) Segregation, independent assortment and crossing over
8. b) Pachytene
9. c) Crossing over
10. b) Crossing over
Tags:
cell biology mcq
cell cycle mcq
mcq on cell biology
MCQ on Cell Cycle
MCQ on Cell Division
mcq on meiosis
mcq on mitosis
meiosis mcq
mitosis mcq