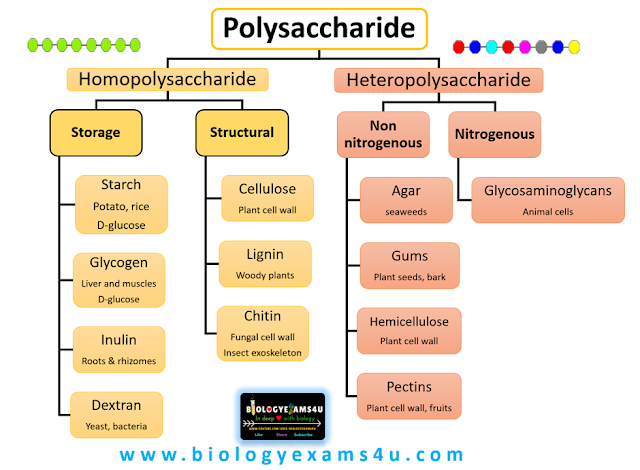
MCQ on Polysaccharides
1. Which of the following is a TRUE statement about
cellulose?
(a) It is easily digestible by humans.
(b) It is the main component of animal cell walls.
(c) Made up of unbranched chains of glucose units linked by β-1,4
glycosidic bonds.
(d) It is used as a storage form of energy in plants.
2. What is the primary difference between starch and
glycogen in terms of structure?
(a) Starch is a homopolysaccharide, while glycogen is a
heteropolysaccharide.
(b) Starch is a linear molecule, while glycogen is branched.
(c) Starch is stored in the liver, while glycogen is stored
in muscles.
(d) Starch is a component of fruits, while glycogen is found in animals.
Detailed Notes of Polysaccharides hereVideo: Classification of Polysaccharides
3. Agar, a commonly used gel in scientific experiments, is
extracted from:
(a) Red algae
(b) Brown algae
(c) Green algae
(d) Blue-green algae
4. Heparin, an anticoagulant drug, is an example of a:
(a) Storage polysaccharide
(b) Structural polysaccharide
(c) Functional polysaccharide
(d) Monosaccharide
5. Chitin, the main component of insect exoskeletons, is
made up of:
(a) Glucose
(b) Fructose
(c) Galactose
(d) N-acetylglucosamine
6. What is the role of glycosidic bonds in polysaccharides?
(a) Provide structural support within the molecule
(b) Link monosaccharides together to form chains
(c) Facilitate enzymatic digestion of the molecule
(d) All of the above
7. Which of the following statements is NOT true about
inulin, a plant fructan?
(a) It acts as a prebiotic, promoting the growth of
beneficial gut bacteria.
(b) It is readily digestible by humans, providing a quick
source of energy.
(c) It can be extracted from chicory root.
(d) It forms branched chains of fructose molecules.
8. Hyaluronic acid, a key component of skin and joints, is a
type of:
(a) Starch
(b) Cellulose
(c) Glycosaminoglycan
(d) Fructan
9. What is the main reason why cellulose cannot be directly
digested by humans?
(a) It lacks essential vitamins and minerals.
(b) It has a complex branched structure.
(c) Human stomachs lack the necessary enzymes for breakdown.
(d) It is toxic to human cells.
10. Which of the following is a homopolysaccharide of
microbial origin made up of glucose units primarily linked by α-1,6
glycosidic bonds ?
(a) starch
(b) dextran
(c) glycogen
(d) inulin
11. Which of the following statements best describes the
relationship between the structure and function of a polysaccharide?
(a) Specific arrangements of sugar molecules determine the
overall shape and function of the molecule.
(b) The type of glycosidic bonds used impacts the
flexibility and solubility of the polysaccharide.
(c) The presence of side chains can modify the molecule's
interactions with other molecules.
(d) All of the above
12. Which of the following is a non-nitrogenous
heteropolysaccharides present in the middle lamella of plants?
(a) agar
(b) gums
(c) glycosaminoglycans
(d) pectin
Answers:
1. (c) Made up of unbranched chains of glucose units linked
by β-1,4
glycosidic bonds.
2. (b) Starch is a linear molecule, while glycogen is
branched.
3. (a) Red algae
4. (c) Functional polysaccharide
5. (d) N-acetylglucosamine
6. (d) All of the above
7. (b) It is readily digestible by humans, providing a quick
source of energy.
8. (c) Glycosaminoglycan
9. (c) Human stomachs lack the necessary enzymes for
breakdown.
10. (b) dextran
11. (d) All of the above
12. (d) pectin