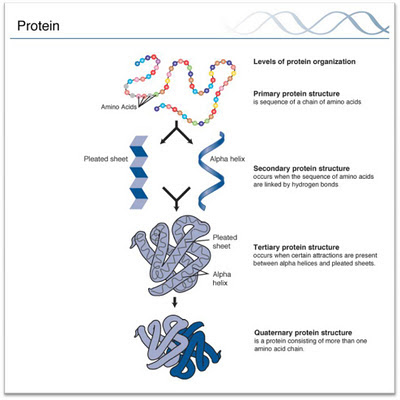
1. The repeating units of proteins are
10. Fibrous protein such as silk fibroin consists of polypeptide chains arranged in
a) glucose units
b) amino acids
c) fatty acids
d) peptides
2. Amino acids are joined by
a) peptide bond
b) hydrogen bond
c) ionic bond
d) glycosidic bond
3. The primary structure of protein represents
a) Linear sequence of amino acids joined by peptide bond
b) 3-dimensional structure of protein
c) helical structure of protein
d) sub unit structure of protein
d) sub unit structure of protein
a) rigid with partial double bond character
b) planar, covalent
c) covalent
d) all of the above
5. Enzymes
are
a) proteins
b) carbohydrates
c) nucleic acids
d) DNA molecule
6. The
first protein sequenced by Frederick Sanger is
a) Haemoglobin
b) myoglobin
c) insulin
d) myosin
7. A
dipeptide has
a) 2 amino acids and 1 peptide bond
b) 2 amino acids and 2 peptide bonds
c) 2 amino acids and 3 peptide bonds
d) 2 amino acids and 4 peptide bonds
8. The
most common secondary structure is
a) α-helix
b) β-pleated
sheet
c) β-pleated
sheet parallel
d) β-pleated sheet non
parallel
9. Myoglobin
is a
a) protein with primary structure
b) protein with secondary structure
c) protein with tertiary structure
d) protein with quaternery structure
10. Fibrous protein such as silk fibroin consists of polypeptide chains arranged in
a) α-helix
b) β-pleated
sheet
c) β-helix
d) none of these
11. α-helix has
a) 3.4 amino acid residues/turn
b) 3.6 amino acid residues/turn
c) 3.8 amino acid residues/turn
d) 3.0 amino acid residues/turn
12. Tertiary
structure is maintained by
a) peptide bond
b) hydrogen bond
c) di-sulphide bond
d) all of the above
a) primary structure
b) secondary
structure
c) tertiary
structure
d) quaternery structure
14. Disulphide bonds are formed
between
a) cysteine residues that are close together
b) cystine residues that are close together
c) proline residues that are close together
d) histidine residues that are close together
15. The
3-D structure of protein can be determined by
a) Nuclear magnetic resonance
b) X-ray crystallography
c) both a and b
d) Spectroscopy
Answers
1-b
|
2-a
|
3-a
|
4-d
|
5-a
|
6-c
|
7-a
|
8-a
|
9-c
|
10-b
|
11-b
|
12-d
|
13-d
|
14-a
|
15-c
|
Tags:
Biochemistry mcq
biochemistry multiple choice
mcq on amino acids
MCQ on Biochemistry
mcq on protein
mcq on proteins
Multiple Choice questions on Proteins
proteins mcq