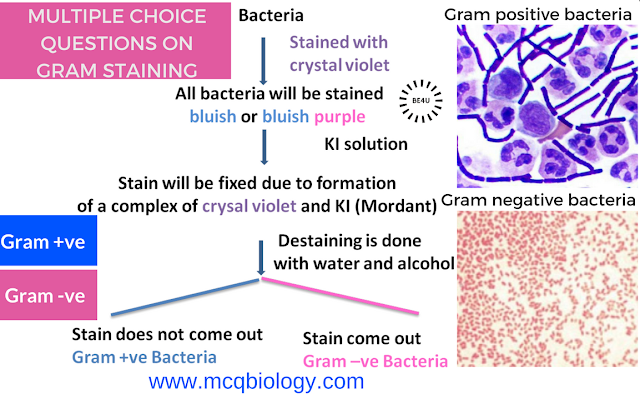
1. Gram staining was developed by
a) French microbiologist Louis Pasteurb) Dutch lens maker Leeuwenhoekc) Danish physician Christian Gramd) Dutch physician Christian Gram
2. Gram staining is an example of
a) Acid fast stainb) Acid stainc) Differential staind) None of the above
3. Gram staining was developed in
a) 1882b) 1883c) 1884d) 1885
4. The most common stains used in Gram staining is
a) crystal violet and methylene blueb) crystal violet and safraninc) crystal violet and carbol fuschind) safranin and methylene blue
 |
| Bacterial cell wall |
5. Which of the following statements are true regarding Gram positive bacteria
a) cell wall has a thick peptidoglycan layerb) cell wall lipid content is very lowc) lipopolysaccharide layer is absentd) all of these
6. Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding Gram negative bacteria
a) cell wall has a thin peptidoglycan layerb) cell wall lipid content is very lowc) lipopolysaccharide layer is presentd) all of these
7. In Gram staining, if some bacteria retain the crystal violet stain after alcohol treatment. Then the bacteria is
a) Gram positiveb) Gram negativec) procedure is incomplete to answer this questiond) none of these
8. Counter stain used in Gram staining is
a) Safraninb) Crystal violetc) carbol fuschind)acetocarmine
9. In Gram staining , the alcohol acts on
a) Teichoic acidsb) Periplasmc) Membrane lipidsd) Peptidoglycan
10. Lipopolysaccharide is found in cell wall of
a) Gram positive bacteriab) Gram negative bacteriac) Bothd) Fungi
11. The differential staining property of Gram staining is primarily due to
a) difference in lipid content in Gram positive and Gram negative bacteriab) difference in protoplasmic contents in Gram positive and Gram negative bacteriac) difference in teichoic acid content in Gram positive and Gram negative bacteriad) all of these
12. In Gram staining iodine is used as a
a) fixativeb) mordantc) solubiulizerd) stain
13. After ethanol treatment Gram negative bacteria can be visualised
a) only by counter staining with safranineb) in violet colour of crystal violetc) only by addition of iodine solutiond) none of these
14. Which of the following is a common Gram positive bacteria
a) Rhizhobium of root nodulesb) Lactobacillus in curdc) Eschericia colid) none of these
15. During ethanol treatment in gram staining,
a) crystal violet stain is dissolved in alcohol in Garm negative bacteria due to high lipid content in the outer layerb) crystal violet stain is retained in Garm positive bacteria due to less lipid content and thick peptidoglycan wallc) both a and bd) none of these
Learn more:
Answers:
2. c) Differential stain
3. b) 1883
4. b) crystal violet and safranin
5. d) all of these
6. b) cell wall lipid content is very low
7. a) Gram positive
8. a) Safranin
9. c) Membrane lipids
10. b) Gram negative bacteria
11. a) difference in lipid content in Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria
12. b) mordant
13. a) only by counter staining with safranine
14. b) Lactobacillus in curd
15. c) both a and b
Tags:
Bacteria MCQ
Gram negative bacteria
Gram positive bacteria
Gram staining mcq
Lipopolysaccharide
MCQ on Gram Staining
MCQ on Microbiology
mcq on Staining
microbiology mcq
Microbiology mcqs